Achilles Tendonitis
Achilles Tendonitis is a painful inflammation of the Achilles tendon at the back (posterior aspect) of the heel and ankle. The Achilles tendon is the largest and most frequently injured tendon in the human body. Often, a bone spur develops in the area where the Achilles tendon inserts/attaches into the heel bone (calcaneus). An ultrasound or an MRI may reveal a tear in the tendon. Removal of the bone spur and repair of the Achilles tendon alleviates the discomfort and allows returning to normal activity.
Ankle/Foot Sprains
Unnatural twisting or trauma to the ankle bones or bones in the feet can stretch or tear the ligaments on the outside or inside or on both sides of your ankle or foot, creating a sprained ankle or sprained foot. Any Sprain that goes untreated can develop into chronic, painful arthritis.
The ankle ligaments stabilize the ankle joint, which stabilizes the knee, hip, and lower back. When these ligaments are torn around the ankle, instability develops which leads to arthritic changes and pain in the ankle joint. New surgical techniques allow the ligaments to be reinforced, repaired, and strengthened on an outpatient basis.
Arthritis
Though the prevalence of arthritis increases with age, arthritis can occur in anyone, regardless of age. Arthritis is characterized by inflammation and swelling of the cartilage and lining of the joints, often along with an increase in the fluid in the joints. Swollen joints stretch the joint capsule (soft tissue envelope around the ankle joint) and corresponding ligaments, which leads to joint instability after the swelling subsides.
Athlete’s Foot (Tinea Pedis)
Athlete’s Foot is a skin disease caused by a fungus that is typically found between the toes and the bottom of the foot. The warm, dark, humid environment in shoes provides an ideal environment for fungus growth.
Symptoms of Athlete’s foot disease are often marked by dry skin, itching, scaling, odor, inflammation, and blisters. If untreated, it can spread to the soles of the feet, the toenails, and even other parts of the body. Fungus particles will make a home in your shoes, so shoes must be disinfected to prevent reoccurrence.
Blisters
Not all blisters need medical attention. You can soothe ordinary blisters with vitamin E ointment or an aloe-based cream. Blisters are caused by friction or minor burns resulting in a bubble of fluid under the skin. The fluid is usually absorbed when the new skin is formed.
Bone Spurs
Bone spurs are an overgrowth of bone resulting from pressure, trauma, or stress on a ligament or tendon attached to the bone. These bony growths are very common and may cause pain and restrict the range of motion around a joint. Bone spurs can be located under a toenail causing pain and deformity to the toenail. Bone spurs, close to the skin surface, can cause a callus or corn when the skin is irritated by rubbing against the spur.
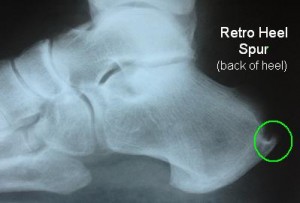
BONE SPUR with pain on the “BACK of the HEEL” (posterior heel, retro-heel, posterior calcaneus, retro-calcaneus)
Achilles Tendonitis is a painful inflammation of the Achilles tendon at the back of the heel and ankle. The Achilles tendon is the largest and most frequently injured tendon in the human body. Often, a bone spur develops in the area where the Achilles tendon inserts/attaches into the heel bone (calcaneus). An ultrasound or an MRI may reveal a tear in the tendon. Removal of the bone spur and repair of the Achilles tendon alleviates the discomfort and allows returning to normal activity.
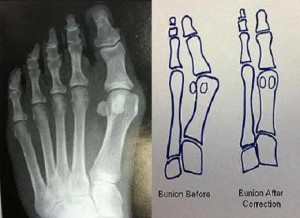
A bunion (pain in the big toe), (Hallux Abducto Valgus), (Hallux Valgus)
Many women and men in America have bunions, a common deformity often blamed on wearing tight, narrow-toed shoes. Bunions cause the base of the big toe to enlarge, often with the skin in the area becoming red and tender. The large toe joint flexes with every step you take making walking painful. The big toe may angle progressively towards your other toes, and in severe cases may overlap adjacent toes.
Bunions: Causes, Prevention, and Treatments
A bunion is an enlargement on the side of the foot near the base of the big toe (hallux) at the metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint. A bunion forms when the bone or tissue at the big toe joint moves out of place. The toe is forced to bend toward the smaller toes, causing a painful lump of bone on the foot. Wearing improperly fitted shoes may be partly to blame for your bunions, but your shoes are not the underlying cause. Heredity plays a major role in the development of a bunion deformity. You do not inherit the bunion, but you inherit the foot type (anatomical blueprints) that may lead to bunions. Pronation and supination are positions your foot adapts during a normal gait cycle. These positions are used about 50/50 during the gait cycle. Frequently, patients with bunions function more on the pronation side than on the supination side. People who suffer from flat feet or low arches are more likely to develop bunions due to excessive pronation. People in occupations that require working on their feet are more prone to develop bunions than those working at a desk.
Some of the signs and symptoms associated with bunions include:
- pain on the inside of your foot at the big toe joint.
- swelling or stiffness to the large toe joint.
- redness on the inside of your foot at the big toe joint.
- numbness or burning in the big toe.
- large toe over/underlapping the adjacent toes
- Range of motion (ROM) to the large toe is less than the (ROM) of the second toe.
Conservative treatments for bunions include the following:
• Wearing the Right Kind of Shoe—Shoes should have a wide, flexible sole to support the foot and provide enough room in the toe box to accommodate the bunion.
• Medications—Anti-inflammatory drugs and cortisone injections can be prescribed by your podiatrist to ease acute pain and inflammation.
• Orthotic Devices—In some cases, custom orthotic devices (arch supports) may be designed by your podiatric physician. ( Insurance approved, custom made orthotics are the contact lens for the feet ).
• Surgical Options—If conservative measures fail and you still have pain that interferes with daily activities, you may need surgery to relieve pressure and return the toe joint to its normal anatomical functioning position.
The most common types of bunion surgery include bunionectomy with osteotomy. Bunionectomy involves shaving/reducing the enlarged portion of the bone and realigning the muscles, tendons, and ligaments. Osteotomy is the preferred choice for moderate to severe bunions and involves making a surgical incision into the bone, repositioning the bone, and securing it into place. If surgery is required, your board-certified foot and ankle surgeon/podiatric physician will discuss your surgical options as well as steps to take for a successful recuperation.
Calluses
A callus is an area of thick, hard skin that can appear on the ball of the foot, the heel, or the outer side of the toes. The callus is often caused by an underlying bone irritation as opposed to being an issue of the skin. Friction and pressure on the skin cause a callus to develop. When the skin is sandwiched between the shoe on one side and the bone spur on the other a corn or callus develops. Removing the spur that is irritating the skin often eliminates the corn or callus formation.
Corns
Corns are a form of callus that forms on the toes when the bones push against the shoe and place pressure on the surrounding skin. There are two kinds of corns: hard and soft. Hard corns are on the top of the toes or on the side of small toes, soft corns resemble open sores and develop between the toes from rubbing against each other. Bone spurs are a common cause. Friction and pressure to an area of the skin cause a protective response by thickening the skin. When the irritation is rapid a blister forms. When the irritation remains for a long time, a callus (corn) develops.
Treatment involves removing the source of the irritation. If a bone spur is irritating the skin, simply removing the bone spur resolves the problem. If a corn/callus develops on a hammertoe, then” hammertoe surgery” solves the problem by straightening the toe and removing the pressure and friction, which created the corn.
Cysts (Ganglionic Cysts)
Cysts are fluid-filled masses under the skin and occasionally can be found in or on tendons and bones. Some cysts connect to nearby joints and tendons making them harder to treat.
DERMATOLOGY
The foot and ankle are common sites for a variety of skin problems. Itchy rashes, contact dermatitis, scabies, insect bites, burns, infections, cuts, frostbite, and warts are just a few of the skin problems we see weekly.
Fallen Arches (Flat Feet), (Flat Foot) (Pes Planus), ( Flexible Foot Instability)
FLAT FEET?
Millions of children and adults have flat feet. Some can walk and function very well; however, the rest of these patients, are unable to work or play without pain in their foot and ankle. In extreme cases, merely walking across their bedroom floor brings tears to their eyes.
Genetics are the blueprints of the body. Foot and ankle problems geneticly run in families. When one or both of the parents have foot problems, the likelihood that their children will have foot problems dramatically increases. When a child inherits the worst genes from both parents, they may develop a flatfoot deformity that is far worse than either parent may have.
Examination of flat feet reveals abnormal alignment problems with the foot, the ankle, and the lower leg. Excessive flexibility with the joints in the foot accounts for the term flexible flatfoot. The foot may appear normal at rest, but it flattens whenever weight bearing occurs. The foot must function as a stable tripod. If one were to draw a line from the heel to the big toe, from the big toe to the small toe and back to the heel, this would form the triangular weight-bearing surface of the tripod. The ankle joint and the leg sitting on top of the tripod. A stable tripod allows the leg to remain vertical and centered over the ankle joint. When the foot cannot support the ankle and the leg, stress develops in the knee, hip, and lower back.
Treatment – the evolution of flatfoot treatment has remarkably improved over the years. Mild cases respond well with doctor prescribed/designed custom-made orthotic devices. Designed from all three of the following, a non-weight bearing cast mold on each foot, a biomechanical examination of each foot, and a tailored orthotic prescription for each foot. This combination helps to create a well-made custom orthotic device. A properly made orthotic realigns and stabilizes the foot, the ankle, and the leg on children and adults. When orthotic control is not sufficient to stop the discomfort, surgical options become necessary. Over the last 100 years, many surgical procedures emerged to address a flatfoot deformity. Unfortunately, each procedure initially viewed itself as the cure for all flat foot problems. As a result, sometimes they worked, but many times, they did not. The current high rate of success in treating flatfoot problems results from incorporating multiple flatfoot procedures together. Stabilizing each weakness or component of the individual’s flatfoot deformity allows the stable tripod to emerge.
Gangrene
Gangrene typically occurs when the blood supply to the foot is lost. The skin, the subcutaneous, and the bone tissues die due to a lack of oxygenated blood and become necrotic. Symptoms may include a change in skin color to red or black, numbness, swelling, pain, skin breakdown, and coolness. The feet and hands are most commonly affected. If the gangrene is caused by an infectious agent it may present with a fever or sepsis. Diabetics are more prone to foot gangrene because they have poor circulation and nerve damage, which allows infections to develop.
Gout (Hyper-uric-acid)
Gout is most commonly found in the big toe joint and more commonly in men than women. It is caused by a buildup of the salts of uric acid – a by-product of a rich protein diet, in the joints. Attacks of gouty arthritis are one of, the most painful forms of arthritis. During an acute gout attack, any movement of the large toe joint causes pain. The gout attack causes the foot to swell, and the skin becomes red, hot, painful, and inflamed. The gout attack closely resembles an infection or trauma around the first MTPJ. Blood tests or biopsy usually clarify the diagnosis.
Treatment: dietary restrictions, medication, changing the current medication used for hypertension if applicable, and surgery.
Hammertoe
Hammertoe is a deformity found in the first, second, third, fourth, and fifth toes. The toe ends up bent at the middle joint giving it the appearance of a hammer. If untreated, hammertoes can require surgery. The hammertoe can develop corns and cause pain in the toes and feet.
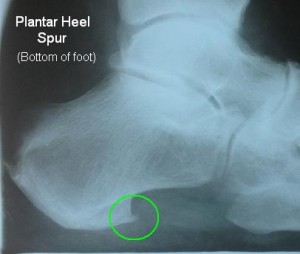
Heel Spurs (Plantar Fascitis) (Heel Pain)
Inflammation of the connective tissue ( plantar fascia) that stretches from the base of the toes, across the arch of the foot, to its insertion into the heel bone (the calcaneus ) is called plantar fasciitis. Also referred to as “heel spur syndrome” this condition is treated with anti-inflammatory medications, ice, stretching exercises, orthotic devices, physical therapy, and occasionally surgery.
Ingrown Nails (onychia), (Paronychia), (Onychocryptosis)
Ingrown nails are nails whose corners or sides dig painfully into the skin and cause infection. They can occur as a result of improper nail trimming, shoe pressure, injury, fungus infection, poor foot structure, and hereditary conditions.
Ingrown toenails are a common problem for children and adults. The shape of the nail plate is a major factor in causing an ingrown nail. A normal nail resembles a dinner plate laying upside down. The outer edges of the nail should be easy to see and easy to trim.
When a nail incurvates or bends inward on the edges the potential for an ingrown nail increases.
Improper trimming can lead to the nail growing into the flesh.
TREATMENT:
The ingrown toenail is gently trimmed away under local anesthesia in the office. A topical medication is applied to the area, preventing the return of the ingrown nail. A Band-Aid with topical medication are used until healing is complete. The entire procedure takes less than 15 minutes. Pediatric and adult patients may return to work or play the same day, and rarely is a pain medication required.
If you think you have an Ingrown Toenail please call our office so we can help you become pain-free. (708) 867-3338
In toeing (Pediatric gait problems, Pigeon toe walking)
Intoeing is a condition that is commonly outgrown by young children without the use of special shoes or treatments. It is a condition caused by the feet pointing inward while running or walking. In many cases, the frog leg style sitting habits of kids are to blame. Most children will outgrow the problem by 8 years of age.
Lesions
The majority of pigmented areas are simple freckles and moles, but some pigmented lesions found on lower extremities could be forms of malignant melanoma. Be mindful of pigmented lesions that suddenly appear or start to change appearance.
Neuroma
Do you have pain in the ball of your foot? Do you have: burning, tingling, numbing type pain in your toes? You may have a neuroma! ((Morton’s Neuroma)
A neuroma is a common problem located between the base of the toes and the ball of the foot. The usual location is between third and fourth toes.
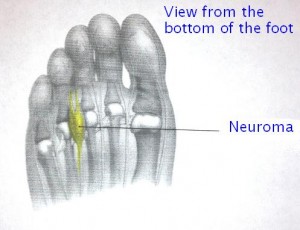 Cause: The outer layer of the nerve rubs against the ligaments as the toes bend upward with each step. Over time repetitive motion causes a thickening of the outer layer of the nerve. The activity increases the size of the nerve within the small space allowed. Women who wear a high heel or narrow-toed, dress shoes with thin soles are great candidates to develop this condition.
Cause: The outer layer of the nerve rubs against the ligaments as the toes bend upward with each step. Over time repetitive motion causes a thickening of the outer layer of the nerve. The activity increases the size of the nerve within the small space allowed. Women who wear a high heel or narrow-toed, dress shoes with thin soles are great candidates to develop this condition.
Symptoms: usually vary from burning, tingling type pain to numbness, or a bruised feeling. The condition is aggravated by activity and diminishes with rest.
Clinical testing: squeeze the ball of the foot from side to side .And at the same time push upwards on the ball the foot near the third and fourth toes. Intense pain or a clicking sensation indicates a neuroma is present.
Treatment options:
1. Orthotics or soft shoes
2. Cortisone injections
3. Physical therapy
4. Surgical removal
Neuropathy
Neuropathy is the loss of feeling pain, heat, or cold in the feet. Diabetes is one common cause of this condition and if left untreated can lead to serious infection.
Plantar Fasciitis (Heel Pain on the bottom of the foot)
Classic symptoms of acute plantar fasciitis are:
-
- intense pain the first time you stand in the morning.
- the pain improves slowly as you walk around.
- the pain slowly intensifies throughout the day.
- pain is worst if you press on the bottom inside half of the heel, about four fingers forward from the back of the heel.
Inflammation of the connective tissue on the plantar surface ( bottom of the foot), which stretches from the base of the toes, across the arch, to the insertion on the heel bone, is called plantar fasciitis. Also referred to as “heel spur syndrome,” this condition is treated with anti-inflammatory medications, ice packs, stretching exercises, orthotic devices, night splints, coblation therapy, shockwave therapy, physical therapy and surgery.
Shin splints
Characterized by pain on either side of the leg bone, Shin splints on the inside of the leg are often related to excessive foot pronation (collapsing arch) but may be related to a muscle imbalance between opposing muscle groups in the leg as well. Shin splints on the front or outside leg area are usually due to overstriding, running up the hill, and running on hard surfaces.
TREATMENT: Proper stretching, icing, strengthening, shortening the stride, and corrective orthotics for pronation can help prevent and treat shin splints.
Smelly Stinky Feet
The interaction between your perspiration and the bacteria that thrive in your shoes and socks generates the odor. Proper treatment of this condition must address both the sweating and the footwear. Smelly feet may also be a result of an inherited condition called hyperhidrosis or excessive sweating.
Stress Fractures
Stress fractures are incomplete cracks in the bone as a result of overuse. With complete rest, stress fractures heal quickly. If left untreated, a stress fracture can become a complete fracture that requires casting and immobilization, and sometimes surgery.
Swelling (Edema) (Water retention)
Edema, swelling of the feet, the legs, and the ankles, is usually caused by an abnormal buildup of fluids in the tissues. Problems with the heart, kidneys, liver, veins, lymphatics system, trauma, arthritis, and hormonal systems are common causes of edema. Painless swelling is a common problem and even more common in the elderly. Swelling can affect one or both legs. A swollen foot is never normal; however, the edema may be the result of gravity and a much larger problem higher up in the leg.
TRAUMA
A fracture (broken bone) in the foot or ankle can be painful and debilitating. Proper alignment and immobilization are essential to proper healing. Sometimes surgery is required to stabilize and correct the misalignment, so the bone can heal.
Ulcers Skin (Diabetic Ulcers) (Pressure Ulcers)
Skin ulcers are sores that have a loss of the epidermis, dermis, or subcutaneous fat tissue. Diabetic ulcers are well known to heal slowly. When the skin on the foot is subjected to increased pressure and friction, the skin tries to develop a protective callus. The callused skin can be subjected to forces that cause separation between layers of skin which fill with fluid and become contaminated and infected.
Warts
A wart is a viral infection that can appear anywhere on the skin. Most foot warts are harmless. Plantar warts or warts found on the bottom of the foot that can be quite painful. Warts are highly contagious. Warts are caused by the Papovavirus and live in the epidermal (outer skin layer) tissues.
Signs to look for if you suspect warts:
- Cauliflower appearance.
- Skin fingerprint lines separate around a wart, like ocean water around an island coming out of the sea. A callus has the lines running through itself.
- Squeezing a wart causes pain, Direct pressure is not as tender as squeezing.
- Black dots represent traumatized blood vessels created by the wart.
Treatment options are numerous and include, freezing, cautery, acids, shaving, excision, topical medications, oral medications, and laser treatments. Dr. Forni offers a variety of treatment options, but prefers shaving warts, when possible. When warts are shaved away, just one visit is usually sufficient to resolve the problem.